Eucaby Architecture
Eucaby consists of three separate applications. The core is Eucaby API which serves messages between users and integrates external web services. Mobile application is the main client which sends and receives user location messages. Eucaby website provides general information and allows to view messages sent to email address.
Before we start feel free to download Eucaby mobile application from Google Play or Apple AppStore and check out the website www.eucaby.com.
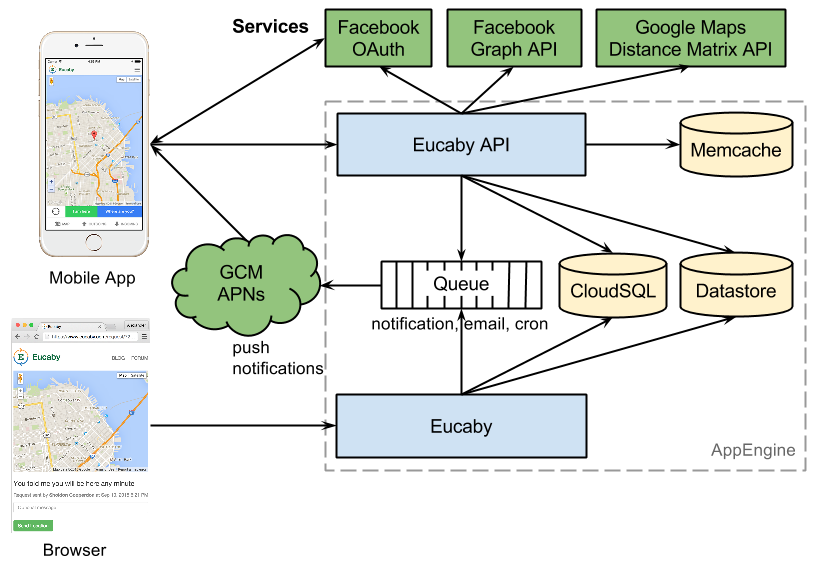
Eucaby API
Overview
Eucaby API runs on Google AppEngine which provides scalable infrastructure and essential architecture components for real-time communication. A real-time messaging consists of several steps:
- User sends location message from mobile device (or browser).
- Message is stored in Cloud Datastore and notification is sent to Task Queue.
- Notification in Task Queue is processed and sent to push notification service (GCM or APNs).
- Notification is delivered to the recipient mobile device.
Components
Eucaby API uses three types of storage: Cloud SQL, Cloud Datastore and Memcache. Cloud SQL is mostly used to store high integrity data such as user and device data. Cloud Datastore, a NoSQL database, stores user messages and locations which don’t require high data integrity or complex queries but require high scalability and performance. Memcache, a key-value storage, is mostly used to cache data from proxy requests to external services such as Facebook Graph API or Google Maps Distance Matrix API.
Operations which can be handled outside of the request are precessed in the Task Queue. This includes push notifications, email notifications and cron jobs. Here is the example of notification task to GCM:
import flask
import logging
from flask import views
from flask import current_app
from gcm import gcm
from sqlalchemy import exc
from eucaby_api import args as api_args
from eucaby_api import models
from eucaby_api.utils import utils as api_utils
class GCMNotificationsTask(PushNotificationsTask):
"""Push notifications for GCM."""
def post(self): # pylint: disable=no-self-use
res = self.handle_input(api_args.ANDROID)
if isinstance(res, flask.Response):
return res
regs = {}
for dev in flask.request.devices:
regs[dev.device_key] = dev
data = api_utils.gcm_payload_data(
flask.request.sender_name, flask.request.message_type,
flask.request.message_id)
gcm_app = gcm.GCM(current_app.config['GCM_API_KEY'])
try:
resp = gcm_app.json_request(
registration_ids=regs.keys(), data=data, retries=7)
except gcm.GCMException as e:
logging.error(
'Failed to push notification. %s: %s',
e.__class__.__name__, e.message)
return e.message, 500
msg = 'GCM result: {}'.format(str(resp))
if 'errors' in resp:
for error, reg_ids in resp['errors'].items():
if error in ['NotRegistered', 'InvalidRegistration']:
# Deactivate multiple devices
for reg_id in reg_ids:
regs[reg_id].deactivate()
if 'canonical' in resp:
for reg_id, canonical_id in resp['canonical'].items():
# Replace registration_id with canonical_id
device = regs[reg_id]
device.device_key = canonical_id
models.db.session.add(device)
try:
# Note: From time to time GCM garbage collects registration
# ids by issuing a new canonical id which replace
# other registration ids for the same device. You
# need to deactivate the devices
models.db.session.commit()
except exc.IntegrityError:
models.db.session.rollback()
device.deactivate()
return msg
Authentication
Authentication Flow Diagram
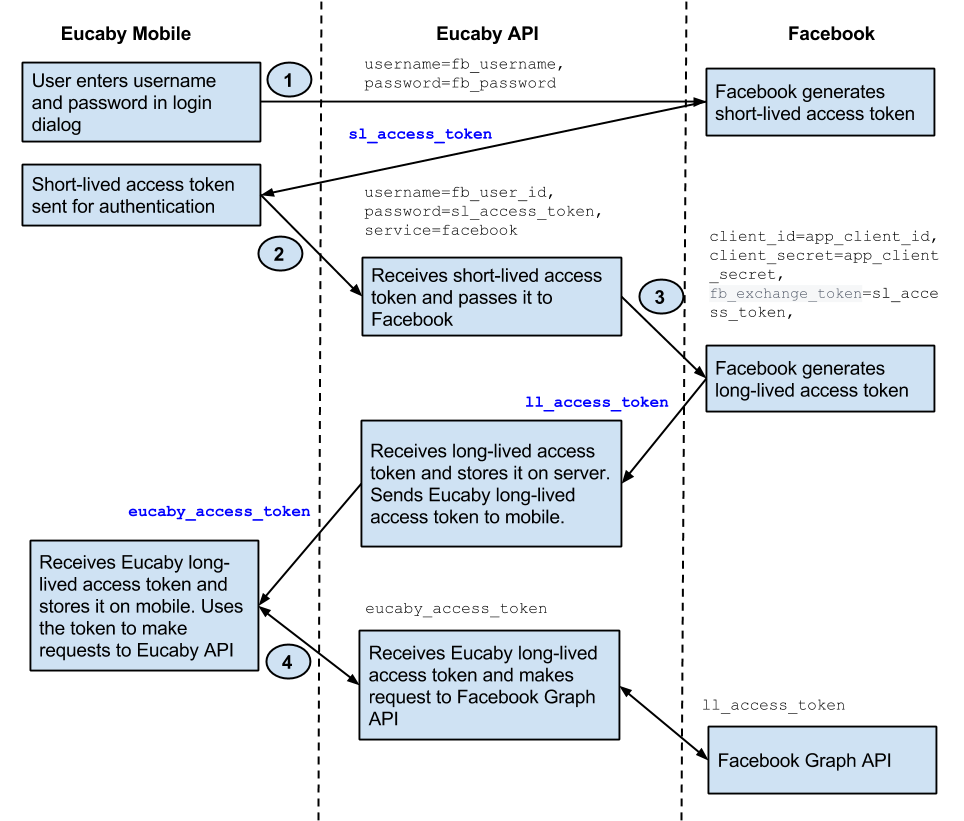
Facebook implements non-standard OAuth with two types of access tokens: short-lived (sl_access_token) and long-lived (ll_access_token) described in Facebook Access Tokens. Eucaby API authentication uses Facebook authentication as follows:
- Request short-lived access token from Facebook using username and password.
- Exchange short-lived access token for long-lived access token and store it for further Facebook Graph API requests.
- Create Eucaby access token and return it back to mobile device for further Eucaby API requests.
Authentication Components
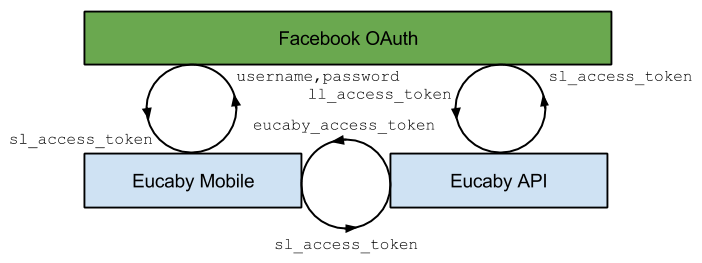
Every access token has limited lifetime. This equally relates to Facebook short-lived and long-lived and Eucaby access tokens. After access token is expired it has to be either refreshed or created again. Eucaby API takes care of it by automatically refreshing access tokens.
Endpoints
Originally I planned to use Google Endpoints because it is really easy to implement API with. But it has one disadvantage that is hard to get around: all endpoints will start with /_ah/api which is no problem for programming interface but makes the REST API not very esthetic. One way to solve the issue is to use redirect for every request but I decided to take a different approach and use Flask Restful instead. It has all essential features to build API but lacking a bit of validation.
Mobile Application
Mobile application is implemented with the popular Ionic framework which is one layer on the top of PhoneGap. It is really easy to use if you get along with AngularJS and allows to generate native code for several mobile platforms out of the box. It supports plugin architecture so you can use pretty much any mobile native functionality with a simple javascript interface. I used a few plugins including PushPlugin for receiving push notifications from GCM or APNs and Geolocation for accurate geographic location. It is perfect for rapid prototyping and conveying ideas.
I noticed a few disadvantages building mobile application with Ionic compared to native application:
- Larger memory footprint. PhoneGap runs embedded browser.
- Slower.
- Quirky. Some interactions look unusual.
AngularJS module which communicates with Eucaby API application is EucabyApi. It uses OpenFB module to authenticate with Facebook OAuth. Mobile application doesn’t use Facebook Graph API directly though. Here is the snippet of the code for EucabyApi module:
angular.module('eucaby.api', [
'openfb',
'eucaby.utils',
'eucaby.config'
])
.factory('EucabyApi', [
'$http',
'$q',
'OpenFB',
'utils',
'storageManager',
'config',
function ($http, $q, OpenFB, utils, storageManager, config) {
return {
init: function(){
OpenFB.init(config.FB_APP_ID,
'http://localhost:8100/oauthcallback.html');
},
login: function(force){
var deferred = $q.defer();
var accessToken = storageManager.getAccessToken();
if (accessToken && !force) {
deferred.resolve(accessToken);
} else {
/*
* Get short-lived Facebook access token
* Get Facebook user profile with '/me' request
* Get Eucaby access token
*/
// ...
OpenFB.login('email,user_friends,public_profile')
.then(function(){
// ...
});
}
return deferred.promise;
},
api: function(obj){
/*
* Ensure that Eucaby access token exists
* Refresh Eucaby access token if it is expired
* Make API request
*/
var self = this;
var method = obj.method || 'GET';
var params = obj.params || {};
var data = obj.data && utils.toPostData(obj.data) || '';
var deferred = $q.defer();
// ...
var apiRequest = function(method, path, token, params){
return $http({
method: method, url: config.EUCABY_API_ENDPOINT + path,
params: params, data: data,
headers: {'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + token}});
};
var makeApiRequest = function(data){
// ...
apiRequest(method, obj.path, token, params)
.success(function(data){
deferred.resolve(data);
});
};
self.login().then(makeApiRequest);
return deferred.promise;
},
logout: function(){
// ...
OpenFB.logout();
}
};
}]);
Eucaby Website
Eucaby website application not only displays general information but also allows users to view or send location message back to the sender. It is implemented in Django and uses some shared resources with Eucaby API.
I am here
